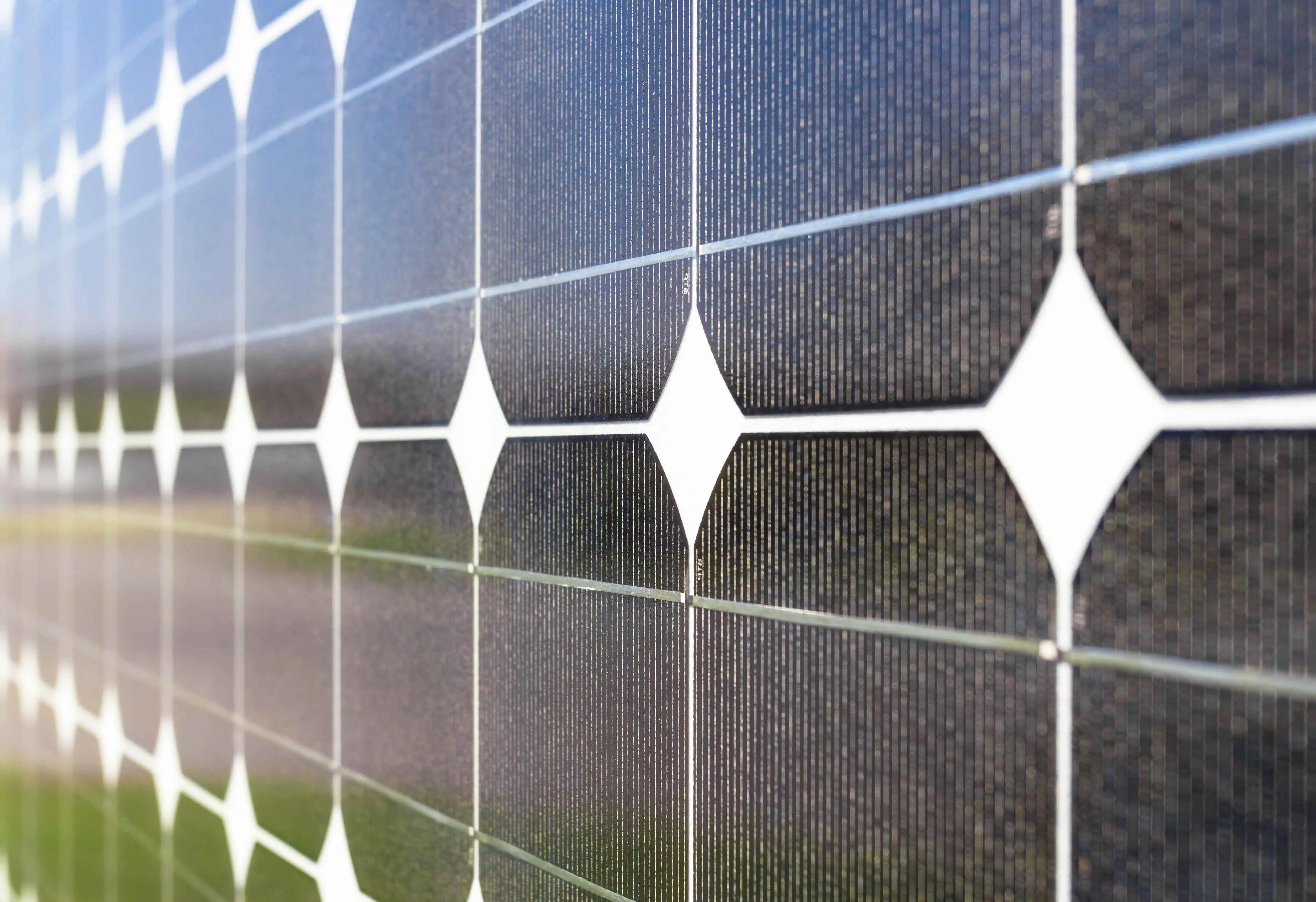
In the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, solar power has emerged as a beacon of hope, offering clean and renewable electricity to homes and businesses worldwide. At the heart of this revolution are solar panels, the catalysts for converting sunlight into usable electricity.
Among the diverse array of solar panel technologies available, two contenders stand out: monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. In this insightful exploration, we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of these two technologies, examining their unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks.
Join us as we delve into the world of monocrystalline versus polycrystalline panels, empowering you to make informed decisions in harnessing the power of the sun.
What will we consider in this article?
What are Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline Solar Panels?
Monocrystalline solar panels are crafted from a single continuous crystal structure, giving them a sleek black appearance and high energy efficiency. The key to their superior performance lies in their purity and uniformity, allowing for greater electron mobility and thus higher energy conversion rates.
This makes them ideal for situations where space is limited, as they require fewer panels to generate the same amount of electricity as polycrystalline panels.
On the other hand, Polycrystalline Solar Panels are made from multiple silicon fragments melted together, resulting in a blue-ish hue and slightly lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels. Despite their lower efficiency, polycrystalline panels offer a more cost-effective option, making them suitable for larger installations where space is not a constraint. While they may not perform as well as monocrystalline panels in low-light conditions, they still provide reliable energy generation and are a popular choice for many solar projects.
Usage of Monocrystalline vs Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline Panels |
|---|
Ideal for residential rooftops with limited space or aesthetic considerations. |
Recommended for off-grid setups where high efficiency and power generation are crucial due to limited space or energy demands. |
Preferred for commercial rooftops or spaces where maximizing energy production within limited area constraints is essential. |
Polycrystalline Panels |
Suited for residential installations where maximizing cost-effectiveness is a priority and ample space is available. |
Suitable for off-grid applications with larger available space and moderate energy requirements, prioritizing cost- effectiveness. |
Appropriate for larger commercial installations where upfront cost savings are prioritized over slightly lower efficiency. |

Pros and Cons (2024)
Monocrystalline Panels:
Pros:
High Efficiency: Monocrystalline panels continue to lead the market with their superior efficiency, maximizing energy production per
square foot of space.
Longevity: With advancements in manufacturing techniques, monocrystalline panels boast a longer lifespan, offering reliable
performance for decades.
Space Efficiency: In urban environments where space is at a premium, monocrystalline panels shine, providing ample power generation in limited rooftop areas.
Cons:
Higher Initial Cost: While prices have become more competitive over the years, monocrystalline panels still tend to have a higher
upfront cost compared to polycrystalline alternatives.
Temperature Sensitivity: While prices have become more competitive over the years, monocrystalline panels still tend to have a higher
upfront cost compared to polycrystalline alternatives. While prices have become more competitive over the years, monocrystalline panels still tend to have a higher
upfront cost compared to polycrystalline alternatives.
Production Constraints: Despite technological advancements, production capacity for monocrystalline panels may still lag behind
demand in certain regions, leading to supply chain challenges.
Polycrystalline Panels:
Pros:
Cost-Effectiveness:Polycrystalline panels remain a budget-friendly option for solar installations, offering
competitive pricing without sacrificing performance.
Improved Efficiency: Ongoing research and development efforts have led to enhancements in polycrystalline
panel efficiency, narrowing the gap with monocrystalline counterparts.
Widespread Availability: With established manufacturing processes and widespread adoption, polycrystalline
panels are readily available in the market, making them accessible to a wide range of consumers.
Cons:
Lower Efficiency: Despite improvements, polycrystalline panels generally exhibit lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels, resulting in slightly reduced energy production.
Aesthetic Considerations:The blue hue of polycrystalline panels may not appeal to all consumers, particularly
those seeking a sleek and uniform appearance for their solar installations.
Limited Lifespan:While durable, polycrystalline panels may have a shorter lifespan compared to monocrystalline
panels, necessitating earlier replacement and maintenance.
Efficiency comparison (Monocrystalline vs Polycrystalline Solar Panels)
Efficiency is a critical factor to consider when choosing between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels. Monocrystalline panels typically boast higher efficiency ratings, often ranging from 15% to 22%, due to their uniform crystal structure and higher purity silicon material.
This superior efficiency translates to greater power output per square meter of panel area, making monocrystalline panels an attractive option for installations with limited space or where maximum power generation is a priority.
On the other hand, polycrystalline panels typically have slightly lower efficiency ratings, typically ranging from 13% to 18%, due to their manufacturing process, which involves casting silicon into molds rather than growing single crystals.
While polycrystalline panels may have lower upfront costs, their lower efficiency means they require more panel area to achieve the same power output as monocrystalline panels. Understanding the efficiency differences between these panel types is essential for selecting the most suitable option based on energy needs, space constraints, and budget considerations.
Price and costs Analysis
Aspects | Monocrystalline Panels | Polycrystalline Panels |
|---|---|---|
Initial Cost | Generally higher | Typically more budget-friendly |
Long-Term Savings | Higher efficiency leads to lower overall costs over the lifespan | Lower efficiency may result in slightly higher long-term costs |
Maintenance Costs | Minimal maintenance required due to durable construction and longevity | Minimal maintenance required due to durable construction and longevity |
Installation Costs | May require fewer panels due to higher efficiency | May require more panels to achieve desired power output |
Ensuring Quality :Trustable Devices
Certifications: Look for solar panels that have been certified by reputable organizations, such as the International Electromechanical Commission (IEC) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These certifications ensure that the panels meet industry standards for performance and safety.
Warranties: Opt for solar panels that come with robust warranties, including performance warranties and product warranties. A performance warranty guarantees that the panels will maintain a certain level of efficiency over time, while a product warranty covers defects and malfunctions.
Reputable Manufacturers: Choose solar panels from well-established manufacturers with a track record of producing high-quality products. Research the manufacturer’s reputation, customer reviews, and history in the industry to ensure reliability and longevity.
Independent Testing: Look for solar panels that have undergone independent testing and evaluation by third-party laboratories. Independent testing provides unbiased assessments of a panel’s performance and reliability, giving consumers confidence in their investment.
Longevity: Consider the longevity of the solar panels, including factors such as durability, weather resistance, and degradation rates. Panels with a longer lifespan are more likely to provide reliable performance and consistent energy production over the years.
Making an informed Decision
When it comes to choosing between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, the decision you make today will impact your energy future for years to come. By arming yourself with knowledge and understanding the facts, you have the power to make an informed decision that aligns with your energy needs, budget, and long term goals.
Consider factors such as efficiency, price, durability, and warranties carefully, weighing the pros and cons of each option. Remember, the right choice is not always the one with the lowest upfront cost or the highest efficiency rating, but rather the one that best meets your unique requirements and offers the greatest value over time.
Trust in the reliability of certified panels from reputable manufacturers, and don’t hesitate to seek advice from solar professionals or consultants if needed. By taking the time to research, compare, and evaluate your options intelligently, you can embark on your solar journey with confidence, knowing that you’ve made a decision that will benefit you and the planet for years to come.
In closing
In conclusion, the choice between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels is a decision that requires careful consideration of various factors such as efficiency, price, and reliability. Both technologies offer unique advantages and disadvantages, and the best option for your solar installation depends on your specific needs and priorities.
By understanding the differences between these panel types and weighing the pros and cons, you can make an informed decision that maximizes the benefits of solar energy for your home or business. With Al Sabah General Electric leading the way in solar innovation, you can trust in our expertise and commitment to delivering sustainable solutions that power a brighter future for all.